What is glaucoma?
Glaucoma
is an illness of the eye where the strain inside the eye, called the
intraocular pressure (IOP) is expanded. Intraocular pressure is estimated
utilizing an instrument called a tonometer.
What is intraocular tension and how could it be kept up with?
As
well as creating this liquid (fluid humour), the ciliary body contains the
suspensory tendons which hold the focal point set up. Muscles in the ciliary
body pull on the suspensory tendons, controlling the shape and centring
capacity of the focal point.
Fluid
humour contains supplements and oxygen that are utilized by the designs inside
the eye. The overabundance liquid is continually depleted from the eye between
the cornea and the iris. This region is known as the iridocorneal point, or the
filtration, or the seepage point.
The
intra-visual tension remaining parts consistent as long as the creation and
retention or seepage of fluid is equivalent.
For what reason is an expansion in intraocular pressure an issue?
When
intraocular pressure is high it can prompt harm or degeneration of the optic
nerve and retina. This is an issue because the retina can change over pictures into nerve signals and the optic nerve
conveys these signs from the retina to the mind to deliver the vision.
Subsequently, an expansion in intraocular tension will quite often bring about
visual deficiency in the impacted eye in light of the harm to the retina or
optic nerve.
Grouping Glaucoma
Glaucoma
might be grouped in one of two ways:
1. Based on the reason, it very well may
be delegated essential, where outpouring issues are connected to hereditary
anomalies in the seepage pathway, or optional, where another visual illness
(for example focal point luxation, uveitis) diminishes surge.
2. Alternatively, glaucoma can be ordered
by the condition of the waste point. The point might be open (in which case the
obstacle is further downstream), restricted or shut.
These
orders are not simple semantics; rather, they have huge clinical ramifications.
It is conceivable that optional glaucoma might be restored assuming the
essential visual illness is dealt with effectively (for example careful
expulsion of a luxated focal point). More significant, assuming that one-sided
glaucoma is considered auxiliary, it implies the contralateral eye isn't really
in danger.
Then
again, canines with essential glaucoma will require deep-rooted treatment.
Besides, in patients giving one-sided essential glaucoma, the contralateral eye
is almost certain to foster the infection (on normal inside 8 months). In
certain varieties, assessment of the point will assist with deciding if the eye
is in danger of creating essential glaucoma.
The
two arrangement techniques complete one another; in canines, it is feasible to
experience any of the conceivable glaucoma mixes: essential open point,
essential thin point, essential shut point, optional open point and auxiliary
shut point glaucoma.
Essential
glaucoma is incredibly uncommon in felines, and for all pragmatic purposes, cat
glaucoma is constantly an optional infection.
Essential open point glaucoma
Essential
open point glaucoma (POAG) is an acquired infection that has been explored
broadly in beagles, in which it was demonstrated to be an autosomal passive
issue. Notwithstanding, POAG has likewise been recorded in Keeshonds, Norwegian
elkhounds, poodles and different varieties, albeit the method of legacy has not
been set up in these varieties.
As
the name suggests, the point and pectinate tendons in canines with POAG are
typical. It is expected that the surge block, situated in the uveal and
corneoscleral meshworks, is the aftereffect of biochemical changes to the
cellar film in these areas. The infection is ongoing in nature, with IOP
expanding gradually over numerous months or a long time. Albeit the canine
might give buphthalmos or even with auxiliary focal point luxation, vision
often is held in cutting edge phases of this illness.
Essential limited and shut point glaucoma (goniodysgenesis)
Essential
limited point glaucoma is an acquired sickness in American and English cocker
spaniels; level covered, Labrador and brilliant retriever breeds; just as
basset dogs, Samoyeds, chow chows, Great Danes, Siberian huskies and others. A
formative irregularity brings about the arrangement of dysplastic pectinate
tendons, which can be viewed as sheets of tissue crossing the waste point.
During
the principal long periods of life, watery humour leaves the eye through stream
openings in the sheets, however in the end the stream openings neglect to
control watery liquid surge enough, bringing about height in the IOP. Most
canine patients present with an intense assault of glaucoma, including
blockage, oedema, fixed widened students and loss of sight. Albeit just one eye
might be impacted at first, the two eyes ought to be assessed and prophylactic
treatment of the unaffected eye is prudent. Individual assaults in impacted
eyes might be dealt with effectively, yet moderate point limiting and
conclusion might create. In these patients, the drawn-out visualization for
vision is incredibly protected.
Optional glaucoma
In
patients with optional glaucoma, pressure ascends from a block of fluid humour
outpouring brought about by another visual sickness, most normally one of the
accompanyings:
• Focal point luxation. Since the focal
point fills in as a hindrance against the positive progress of glassy, any focal
point luxation (regardless of whether front or back) may permit glassy humour to
move into the foremost chamber and impede surge. On the off chance
that the focal point luxation is foremost, the liquid surge will be additionally
hindered by the actual presence of the focal point in the front chamber.
• Uveitis. In these patients, the
provocative material in the foremost chamber (for example cells, platelets,
fibrin) can impede the iridocorneal point. Also, uveitis can prompt grip
between the iris and the focal point or cornea (back and front synechia,
individually), further disturbing watery humour outpouring.
• Intraocular cancer. Cancers can cause
glaucoma by initiating uveitis. Besides, neoplastic cells can impede the point,
or the growth (if adequately enormous) can truly pack the point. Intraocular
cancers ought to be suspected in any senior patient with one-sided uveitis or
one-sided glaucoma.
Manual for diagnosing glaucoma
Tonometry
(estimating IOP)
In
canine patients, the typical IOP range is 15 to 25 mm Hg. The rise in IOP is
characterized as glaucoma, though low IOP is typically an indication of uveitis
connected to expanded capricious outpouring. The IOP estimation ought to be
comparable in the two eyes. Contrasts of more than 10 mm Hg between eyes
might be demonstrative of glaucoma. Moreover, a typical strain in an eye with
uveitis is dubious, as the hypotensive impact of uveitis might be covering a rise
in pressure.
IOP
can't be estimated carefully with one's fingers. It ought to be recorded by
utilizing a Schiotz (space) tonometer or, ideally, with a cutting edge bounce
back or applanation tonometer.
Gonioscopy
(looking at the iridocorneal point)
It
is critical to look at the point to decide the danger of glaucoma in breeds
with goniodysgenesis, or then again on the off chance that the infection has
effectively evolved in the other eye. Gonioscopy is performed by an expert
utilizing an extraordinary focal point (for example goniolens) that is put on
the cornea. The focal point refracts active light and permits representation of
the whole point to characterize its state.
In
canines with one-sided glaucoma, the infection might be optional; or it tends
to be an essential illness, as one eye is habitually impacted before the other.
Assuming one-sided essential glaucoma is suspected, a reference for gonioscopy is
required so prophylactic treatment can be started in the unaffected eye.
Are sure varieties bound to get glaucoma?
Indeed, the accompanying varieties are related to glaucoma:
- Akita Dalmatian
- Norwegian Elkhound
- Alaskan
- Malamute
- English Cocker Spaniel
- Poodle
- American Cocker Spaniel
- English Springer Spaniel
- Samoyed
- Basset Hound
- Flat-Coated Retriever
- Shar Pei
- Beagle
- Giant Schnauzer
- Shih Tzu
- Boston Terrier
- Great Dane
- Siberian Husky
- Bouvier des
- Flandres
- Greyhound
- Smooth-Haired
- Fox Terrier
- Bull Mastiff
- Italian Greyhound
- Welsh Springer Spaniel
- Chow Miniature
- Pinscher Wirehaired
- Fox Terrier
- Cocker Spaniel
- Miniature Schnauzer
Signs and symptoms
Canine
glaucoma might influence every visual layer and design:
• Torment. Glaucoma is an agonizing
illness. The aggravation can be communicated as blepharospasm or as broad
gloom. While the aggravation might be more treacherous in canines with ongoing
glaucoma, numerous proprietors report an emotional improvement in the
creature's conduct following enucleation of a glaucomatous eye.
•Buphthalmos. Glaucoma might cause an
increment in the size of the globe, coming about because of extending the
collagen strands of the cornea and sclera. Buphthalmos ordinarily happens all
the more as often as possible in patients with a constant infection just as in
youthful patients, as the sclera is more flexible and stretches all the more
without any problem.
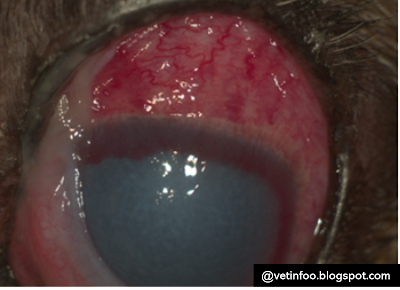
• Clog of veins. The eye will seem red
from the clog of episcleral vessels.
• Corneal pathology. Raised IOP harms
the corneal endothelium, which is answerable for keeping up with corneal drying
out, bringing about oedema (see Figure 4). Extending the corneal strands in
patients with buphthalmos may cause a break of the endothelial cellar film. These
bursts, considered white lines in the cornea, are called striate keratopathy
and are pathognomonic for glaucoma.
• Students. In the beginning phases of the
infection, the student might be enlarged somewhat, and its reaction will be
lazy. In cutting edge or intense phases of the infection, the students are
enlarged and nonresponsive.
• Focal point. The focal point might
luxate (or subluxate) from extending and tearing the zonules. As noticed,
the opposite may likewise be valid, as luxated focal point can cause glaucoma.
•Retina, optic nerve and vision. Glaucoma
will cause decay of the ganglion cell layer and other inward retinal layers.
This decay is an aftereffect of nearby ischemia, brought about by strain on the
retinal veins (the external retina is provided by the choroid and is less
impacted by ischemia). Extra harm to the ganglion cells happens from the crimping
of their axons as they leave the eye at the lamina cribrosa locale. In this
piece of the eye, the impact of raised IOP might be seen ophthalmoscopically as
measuring of the optic circle. Given the harm to the inward (and, in the
long run, external) retina, the patient will experience moderate or intense
loss of vision, which might prompt total visual deficiency.
• End-stage glaucoma. Because of
ongoing IOP rise, the ciliary body might decay, causing diminished fluid
creation, bringing down strain and decay of the eye (phthisis bulbi).
Clinical treatment
Osmotic
diuretics
These
medications are not utilized for long haul treatment of glaucoma. All things
considered, they serve for crisis bringing down of IOP in patients with intense
assaults. The most usually utilized medication in this classification is
intravenous mannitol directed gradually at 1 to 2 g/kg more than 30 minutes;
water is kept for three to four hours.
Prostaglandin
analogues
These
medications act by expanding the unpredictable surge. They are best in canines
because their impact is autonomous of the condition of the point
(which is habitually obstructed). These medications are incapable in felines
since felines come up short on the receptor, and they are contraindicated in
all patients with uveitis. Latanoprost, travoprost and different medications in
this class are regulated more than once per day.
Standards of glaucoma treatment in canines
• The points of glaucoma treatment are to forestall further vision misfortune and diminish the aggravation brought about by IOP rise. Right now, it is difficult to reestablish vision that has been lost because of glaucoma.
• Essential glaucoma requires deep-rooted treatment. The proprietor should comprehend that the illness can never be completely restored and the point of treatment is to balance out the IOP.
• Analysis of essential glaucoma in one
eye orders prophylactic treatment in the other eye. Assuming that you are
questionable, consider alluding to an expert for gonioscopy.
Carbonic
anhydrase inhibitors
Carbonic
anhydrase is a critical chemical in the development of fluid humour and,
consequently, its restraint will bring about lower creation and diminished IOP.
Very much like prostaglandin analogues, this impact is free of the condition of
the point. The skin type of the medication (dorzolamide, brinzolamide) is
controlled double a day and has none of the fundamental secondary effects seen
with the foundational inhibitors.
Effective
miotics
These
medications increment waste by opening the iridocorneal point (through
compression of the iris and ciliary muscle). The most generally utilized
medication in this classification is pilocarpine 1% to 4%, applied a few times
each day.
Beta-blockers
Sympatholytic
drugs lessen fluid creation by decreasing the bloodstream to the ciliary body.
They are regularly utilized in people, yet their viability in creatures is
questionable. Fundamental secondary effects are normal in little canines,
felines and creatures with pneumonic or cardiovascular infection. Sedates in
this classification incorporate timolol, levobunolol and betaxolol, which are
controlled on more than one occasion day by day. A readiness containing timolol
and dorzolamide is monetarily accessible and might be extremely effective.
Regulating
eye drop meds
Regardless of the visual sickness, you are treating, one drop is in every case enough. The
subsequent drop essentially cleans out the first. Assuming that you apply two
drops, you are squandering a large portion of the container and not acquiring
anything.
Hold
the eye open—not shut—for 30 to 60 seconds after ingraining the drops.
Squinting expands the waste of tears and medications from the eye and diminishes
the contact season of the medication with the visual surface.
Careful
treatment
Reference
ophthalmology facilities might do a medical procedure to increment watery humour
outpouring (ordinarily by embedding seepage tubes in the eye) or to diminish
fluid creation through incomplete obliteration of the ciliary body, utilizing
laser or cryotherapy.
Notwithstanding,
as often as possible the (careful or clinical) treatment falls flat, and the
expert is confronted with a visually impaired and agonizing eye. Patient
government assistance requires evacuation of this eye through enucleation.
Proprietors of canines with essential (however not optional) glaucoma might be
offered gutting (for example implantation of a prosthesis in a void scleral
shell) to give a more superficial appearance
Is glaucoma in canines infectious for people or different pets?
Glaucoma
isn't infectious between creatures or even between people. It is innate in
specific varieties, be that as it may.
What is the expense of treating glaucoma in canines?
The
expense to treat glaucoma shifts with the course in which your veterinarian
suggests. Overseeing glaucoma can be costly: With meds, routine tests (subject
matter experts, similar to an ophthalmologist, typically will more often than
not run higher in cost), the expenses can amount to a great many dollars all
through the canine's life. Assuming a medical procedure is vital, while the
underlying expense might be high, it's an expense that is normally not
rehashed. Not all veterinarians charge a similar sum, and geographic area can
assume apart with regards to the expense of treating your canine's glaucoma.
Since
treatment can get costly, pet protection might be a choice. Assuming you don't
as of now have an arrangement, ask concerning whether another arrangement would
cover your canine's condition after an underlying effortlessness period.
When
settling on the best course of treatment, there are a few variables to
consider. Cost, corrective inclination (while eliminating the eye is
important), vision potential, and the kind of glaucoma your canine has all add
up. Since there are no ensures, it's ideal to gauge the expenses with the
possible gains and see what appears to be legit for your canine.
Recuperation and the board of glaucoma in canines
Assuming
the eye should be taken out as the aftereffect of vision misfortune due to
glaucoma, your canine should wear an Elizabethan choker/cone for insurance
until the stitches are taken out.
The
waiting impacts of the sedation and the chance of inconvenience might be
available in the initial not many days after the medical procedure however can be
made do with the drug. An exam is required a couple of days a short time later,
however, the stitches will not be eliminated until following 10-14 days.
Difficulties are uncommon yet at the same time conceivable, albeit most canines who have the medical procedure make a full recuperation.
Assuming
that glaucoma is distinguished early, medicines will be observed, so follow-up
arrangements will be essential for your canine's administration plan. For
breeds inclined to create glaucoma, tests double a year help in early
location.
Whether
or not administration comprises of drug and checking, or making things a stride
further with a medical procedure, the outcome is something similar — to bring
your canine help.
Instructions to forestall glaucoma in canines
Optional
glaucoma can be forestalled by protecting your canine, putting forth a valiant
effort to keep away from wounds and mishaps, keeping steady over medical
problems and searching out therapy for any contamination, particularly eye-related, quickly.
Essential
glaucoma, nonetheless, isn't preventable because it is the
consequence of hereditary qualities. Be that as it may, steps can be taken in
advance to attempt to ease back any degenerative changes to your canine's eyes
and diminish their odds of creating glaucoma.
• Cancer prevention agents like
beta-carotene, nutrients E and C, also as nutraceuticals would all be able to
be taken to lessen the measure of harm that happens to the cells of the eye.
• Diminishing stressors in your pet's
current circumstance can assist with dealing with the oxidative harm that
happens all through the body, including the eyes.
• Killing strain to your canine's neck
is additionally basic since we would rather not increment between cerebral or
intraocular tension through a tight restraint or saddle framework.
• For maturing pets and higher danger
breeds, ensure your veterinarian check your canine's eye tension during health
tests.
Despite
the kind of glaucoma your canine has, early location is the most ideal way to
forestall the movement of the condition and the subsequent visual deficiency
that is frequently connected with glaucoma. Recognizing those unpretentious
strain changes in the eye and tending to restoratively from the get-go, is the
most effective way to forestall further harm.
Is there an immunization for glaucoma in canines?
There
isn't an immunization that treats or forestalls the beginning of glaucoma.
Is follow-up treatment important?
Whenever
glaucoma is analyzed and prescription is begun, follow-up checking will be
important. At first, your veterinarian will prescribe regular subsequent
assessments to guarantee that your canine is reacting satisfactorily to the
treatment or to make acclimations to the prescriptions.
What is the prognosis?
The
anticipation depends to a degree upon the hidden reason for glaucoma. In
the long haul, steady clinical treatment will be needed to monitor the
sickness.















0 Comments